Even before 2020, the education market was rapidly leaning into digitalization. That trend exploded when the pandemic forced education online, requiring every part of the education process to be digitized. Interaction between students and teachers shifted from physical classrooms to entirely digital ones.
Institutions had to work quickly to support this shift. Most either expanded their e-learning platform’s computational capacity to support the influx of users or quickly created new platforms to adhere to “new” digital demand. These e-learning platforms, also known as Learning Management Systems (or LMS’s), already played an important role in educational institutions. However, the pandemic changed their role from “beneficial” to “essential”. While the moves institutions took to support their e-learning platforms helped bridge the gap in a moment of crisis, they were never intended to be a permanent solution.
The digitization of education isn’t slowing down. The LMS market is projected to grow from $16.19 billion in 2022 to $40.95 billion by 2029, at a CAGR of 14.2%, according to Fortune Business Insights. To support this continued growth and create a more stable foundation for e-learning platforms, we need to take a closer look at the environments hosting these platforms. By revising and optimizing these environments, we can offer a solid, supportive infrastructure that improves the experience for students and teachers alike.
Modernizing Moodle with Google Cloud
Introduced in 2002, Moodle is one of the most used e-learning platforms in the world. Moodle is a trusted tool for institutions around the world, but the platform wasn’t designed for the public cloud. This has made scaling difficult. To ensure users can rely on Moodle to continue delivering connected experiences, Google Cloud’s Customer Engineers have developed an open-source, cloud-native approach for hosting Moodle. This brings together the built-in, reliable, and highly scalable services of Google Cloud and Moodle to create a more modern, robust, easy to manage, and cost-effective implementation.
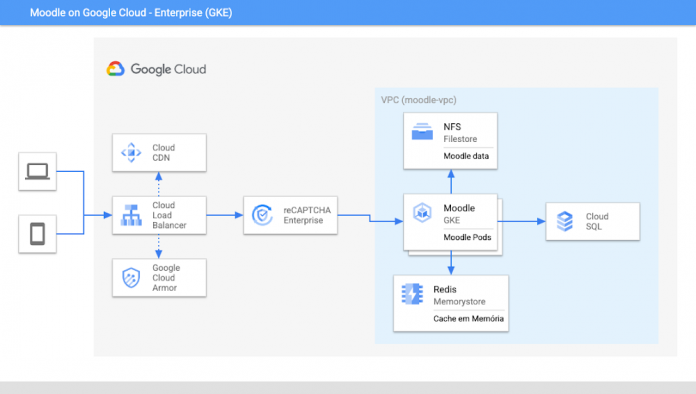
From a technical perspective, this solution incorporates an official Moodle instance into a custom Docker image. This gets deployed into an enterprise version of Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), along with underlying services to support Moodle’s operational and specialized tasks. See Figure 1 below for the complete architecture.
Figure 1. Solution Architecture
Incoming traffic first hits GCP’s Load Balancer. Among other functions, it plays the role of ingress controller for GKE, where Moodle’s pods run.
Load Balancer gets connected with two separate services: Cloud CDN (to deliver static content from pops closer to the requestor, reducing latency) and Cloud Armor, which is a Web Application Firewall (WAF) layer 7, and validates requests against OWASP top ten risks.
If the request is valid from a WAF perspective, it then hits reCAPTCHA enterprise, which will go over an additional access validation. This step is optional, but highly recommended.
Moodle’s web application pods run on top of highly scalable GKE. Moodle’s data files (aka moodledata) sit on a private version of Filestore service in Google Cloud and get accessed dynamically by working those pods in a scalable way. The storage is also shared among all pods.
It also utilizes Memorystore for Redis in Google Cloud for persisting users’ data in memory. This lets Moodle become stateless, allowing it to scale up and down easily.
Last but not least, Moodle’s pods communicate with the instance’s database that lives in a high-scalable version of MySQL (part of Cloud SQL service).
Benefits of modernizing Moodle with Google Cloud
Quick go-to-market. Everything you need to deploy this solution has been scripted and made available in this GitHub repository. That means institutions can simply follow the steps described in the repository’s documentation to get things running quickly. Google Cloud customized every step of the deployment to give you optimal resources and cost savings with the initial setup.
Cloud-native. This implementation of Moodle is 100% cloud-native. That means that all the services utilized by the solution are built-in Google Cloud services—meaning no more Virtual Machine management—and you get all the default benefits enabled within Google Cloud.
Highly scalable. The solution makes Moodle stateless, allowing it to scale up and down with no damage to users’ in-memory data. With GKE, you can also horizontally scale Moodle’s pods and cluster nodes, allowing web applications to always be on. All underlying services can follow GKE’s auto-scalability.
Open-source. The implementation of this solution is publicly available on GitHub. Institutions can collaborate with our engineers, or take it as a starting point for building something tailor-made.
Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Deployment (CD) ready. The solution was designed to work smoothly with DevOps automation practices. For that, Google Cloud recommends leveraging Google Cloud’s Artifact Registry and Cloud Build services.
Multi-sized environment options. We’re starting the project with an enterprise version for Moodle using GKE as the base for running Moodle’s instances. This is most suitable for bigger environments (5,000+ users). We will soon bring Moodle to a serverless model as well, allowing smaller environments and institutions to run at a lower cost.
Security embedded. On top of the web security layer provided by Cloud Armor and reCAPTCHA, modern Moodle deploys in private mode, meaning that all the underlying services supporting Moodle instance get enclosed to its network boundaries. Only internal resources (from the same Virtual Private Network) can access the services.
Bringing a modern Moodle to your institution
It was important to us to keep modern Moodle on Google Cloud an open source solution. Every institution has its own needs based on individual priorities, goals, course needs, and communications preferences, and we wanted to bring together the speed of ready-to-use deployment with the customization needed to make modern Moodle a perfect fit for differing needs. Keeping it open source allows institutions to build their own environments. Simply clone the repository’s content, customize it, and deploy it directly into your Google Cloud accounts.
In addition, Google Cloud-certified partners can help institutions make sure their support needs are covered, including service level agreements, regulatory measurements for compliance and additional layers of security.
Visit GitHub to learn more about modern Moodle with GCP and how it can support your e-learning platform use today.
Cloud BlogRead More