Security has become a critical component in every modern application and platform today. As IT admins try to implement security policies required to protect applications across distributed platforms, they often run into issues such as the lack of effective policy enforcement and lack of visibility into the policy violations. In addition, whenever there is a platform policy change, application operators struggle to figure out the cause of the issues due to the lack of effective policy monitoring capabilities for live deployments.
Anthos is a secure container application platform that runs both on premises and in public clouds, with integrated and easy-to-operationalize security features connected to a centralized control plane in the Google Cloud. Anthos automates policy and security for Kubernetes clusters. Anthos Config Sync reconciles the state of clusters with one or more Git repositories. Policy Controller enables the enforcement of fully programmable policies for your clusters. These features, along with Anthos Service Mesh (ASM) and the Anthos Security dashboard (in Preview), work together to address the security and governance pain points, and help admins and developers to strengthen both the platform and application security posture.
Let’s walk through an example of how to use Anthos to securely deploy an Online Boutique Shop app and apply centralized policies at the same time. The application consists of a number of key services such as frontend, cartservice, checkout service and so on.
Putting your application operator hat on, imagine you want to enable secure service communications, monitor the overall health of the services, create a service-level objective (SLO) alert for your “frontend” service, and drill down to the “cartservice” to troubleshoot a customer issue. ASM can help you do all of the above. It can help simplify service delivery across the board, from traffic management to the compressive mesh telemetry. ASM can also help you embrace a Zero Trust security model. You can manage authentication, authorization, encryption, and communication between services, with little or no changes to the application itself.
Many security administrators want to be able to enforce policies across the platform and audit and eliminate any violations. Security admins want to have centralized governance at scale instead of manually configuring every cluster in their inventory running in the cloud and on-prem.
To achieve the above goals, we recommend first creating policies with the Anthos Policy Controller, which is based on the open source Open Policy Agent Gatekeeper project, and comes with a full library of pre-built policies for common security and compliance controls. Policy Controller also comes with out-of-the-box policy bundles that can audit the clusters against pre-built Kubernetes standards, industry standards, and Google Cloud’s recommended best practices.
Policy Controller can also enforce the clusters’ compliance using objects called constraints. For example, you can create a constraint to make sure all the services in the application have sidecar proxies injection so that the application’s health can be monitored easily. Another example of a constraint is to enforce the traffic encryption with strict mTLS so that all the communications among your application services are secure.
Once the constraints have been created, you can sync them to the clusters with Config Sync. Config Sync can help teams to collaborate with a GitOps model to speed up the overall development cycle. It also can help users apply multiple policy layers. For example, some policies can be applied at the organization level while the others can be applied to a specific namespace.
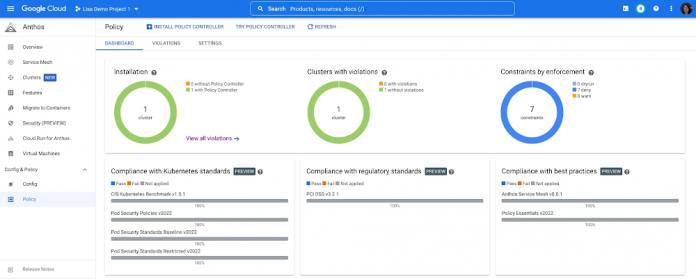
Figure 1 is a snapshot of the Anthos policy dashboard with seven constraints applied to the Anthos cluster, enforcing policies like strict mTLS and sidecar proxy injection in all the services of the online shop app.
You can also just audit a policy without enforcing it. The Policy Controller dashboard shows you a centralized view for all the violations happening across your fleet of clusters and helps take any action if needed. For example, you can enforce granular access control for services so that only designated resources can access each application service. Figure 2 and Figure 3 indicate that there is one policy violation for the application — the istio-system doesn’t have a default deny authorization policy. You can give specific services granular access control to fix the issue so that the red alert in the policy violations dashboard goes away.
In addition to providing continuous audit, Anthos Policy Controller also analyzes resource configurations during the CI/CD cycle. This provides valuable feedback during the process of configuration changes, and ensures any non-compliant changes are caught early in the pipeline. The Binary Authorization feature is another useful Anthos security feature. This deploy-time security control ensures only trusted container images are deployed on production clusters. You can require images to be signed by trusted authorities during the development process and then enforce signature validation when deploying.
Finally, the Anthos Security dashboard provides a fleet-wide view for your Kubernetes network security, binary authorization and mesh policies such as mTLS and authorization based policies, as in Figure 4. Figure 5 shows a more detailed view of workloads’ security configurations that can help improve your security posture.
Google Cloud has powerful security features built in at every level that work separately and together to protect customers’ platform from dangerous exploits. To learn more about how Anthos helps you modernize apps and infrastructure in place, and ensure consistent governance and security achieved at-scale, check out the website here.
Additional resources
Explore the tutorial to learn how to strengthen your application’s security with Anthos
Learn more about Google Kubernete Engine and Anthos
Check out the exciting announcements and sessions from Google Cloud NEXT 2022
Cloud BlogRead More